
Regardless of treatment received (edoxaban or warfarin), patients who met pre-specified clinical criteria for dose reduction had higher rates of stroke or SEE and major bleeding.1 Of patients randomized to edoxaban, 25.4% were dose reduced based on pre-specified clinical factors known to potentially increase the risk of bleeding due to higher drug exposure. The ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 study compared two once-daily edoxaban treatment strategies, a high-dose regimen (60 mg or 30 mg dose-reduced) and a low-dose regimen (30 mg or 15 mg dose-reduced), with warfarin for a median of 2.8 years. The analysis also compared rates of major bleeding and efficacy outcomes of edoxaban versus warfarin, stratified by dose reduction status. Thursday, September 4, 2014, 14:00 Hrs ĭaiichi Sankyo Company, Limited announced data from a subgroup analysis of the phase 3 ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 study, that explores the relationship between edoxaban dose, concentration and anti-factor Xa activity in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). Click hereĭaiichi Sankyo announces data from subgroup analysis of phase 3 ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 study
(Funded by Daiichi Sankyo Pharma Development ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 number, NCT00781391.).You can get e-magazine links on WhatsApp. The corresponding annualized rates of death from cardiovascular causes were 3.17% versus 2.74% (hazard ratio, 0.86 95% CI, 0.77 to 0.97 P=0.01), and 2.71% (hazard ratio, 0.85 95% CI, 0.76 to 0.96 P=0.008), and the corresponding rates of the key secondary end point (a composite of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes) were 4.43% versus 3.85% (hazard ratio, 0.87 95% CI, 0.78 to 0.96 P=0.005), and 4.23% (hazard ratio, 0.95 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.05 P=0.32).īoth once-daily regimens of edoxaban were noninferior to warfarin with respect to the prevention of stroke or systemic embolism and were associated with significantly lower rates of bleeding and death from cardiovascular causes. The annualized rate of major bleeding was 3.43% with warfarin versus 2.75% with high-dose edoxaban (hazard ratio, 0.80 95% CI, 0.71 to 0.91 P<0.001) and 1.61% with low-dose edoxaban (hazard ratio, 0.47 95% CI, 0.41 to 0.55 P<0.001). In the intention-to-treat analysis, there was a trend favoring high-dose edoxaban versus warfarin (hazard ratio, 0.87 97.5% CI, 0.73 to 1.04 P=0.08) and an unfavorable trend with low-dose edoxaban versus warfarin (hazard ratio, 1.13 97.5% CI, 0.96 to 1.34 P=0.10). The annualized rate of the primary end point during treatment was 1.50% with warfarin (median time in the therapeutic range, 68.4%), as compared with 1.18% with high-dose edoxaban (hazard ratio, 0.79 97.5% confidence interval, 0.63 to 0.99 P<0.001 for noninferiority) and 1.61% with low-dose edoxaban (hazard ratio, 1.07 97.5% CI, 0.87 to 1.31 P=0.005 for noninferiority). The principal safety end point was major bleeding. Each edoxaban regimen was tested for noninferiority to warfarin during the treatment period. The primary efficacy end point was stroke or systemic embolism.
#Engage af timi 48 trial
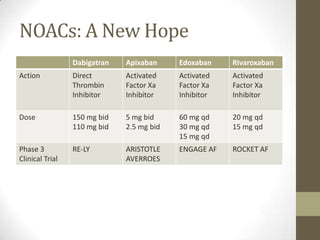
We conducted a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy trial comparing two once-daily regimens of edoxaban with warfarin in 21,105 patients with moderate-to-high-risk atrial fibrillation (median follow-up, 2.8 years). The long-term efficacy and safety of edoxaban as compared with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation is not known. Edoxaban is a direct oral factor Xa inhibitor with proven antithrombotic effects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
